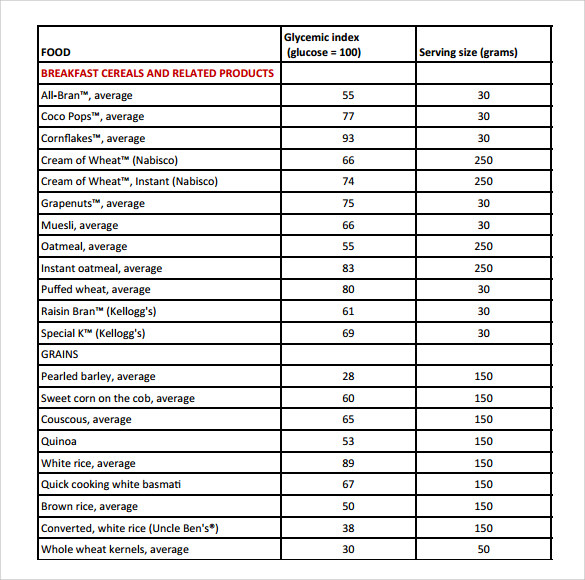
Low gi (55 or less) choose most often. The glycemic load (gl) adds the amount of carbohydrate (quantity) into the. A low gi is a sign of better quality. Foods are categorized as low gi (55 or less), medium gi (56 to 69) and high gi (70 or more). Eating foods with a lower gi may result in a more gradual rise in your blood sugar level.
Web this page provides a comprehensive gi index chart and their corresponding glycemic index and glycemic load values for easy reference. Web glycemic index (gi) is an objective way of measuring this effect. Foods with a higher gi value are more likely to spike your blood sugar than foods with a lower gi. Crease blood sugar higherand faster. Web glycemic load chart below should be used as a guide to make wiser food choices to perform better all day long and feel better generally by keeping your blood glucose levels relatively constant.
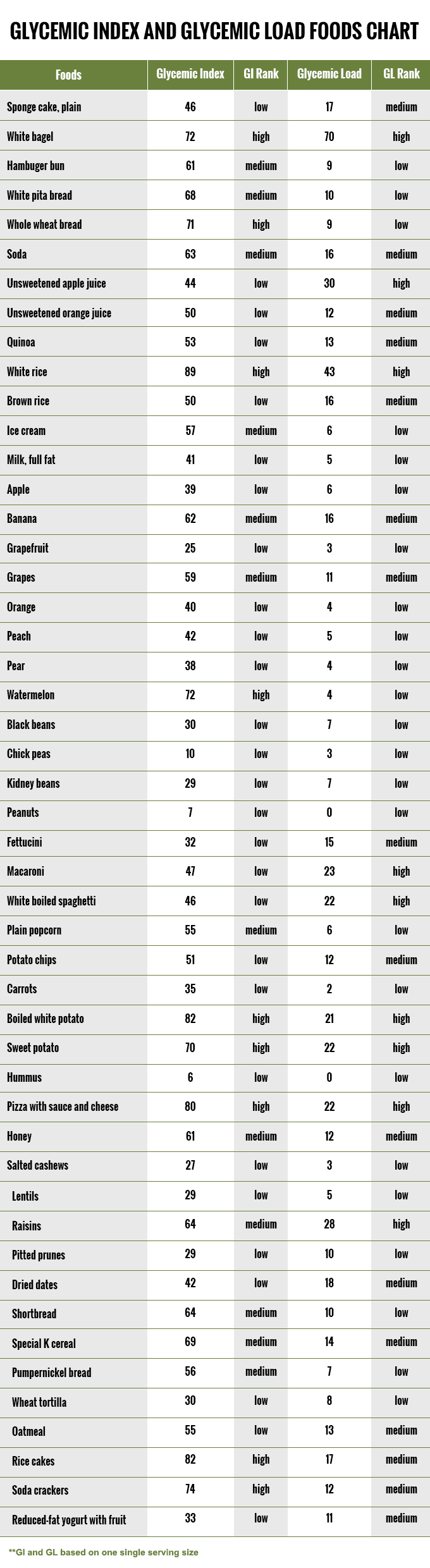
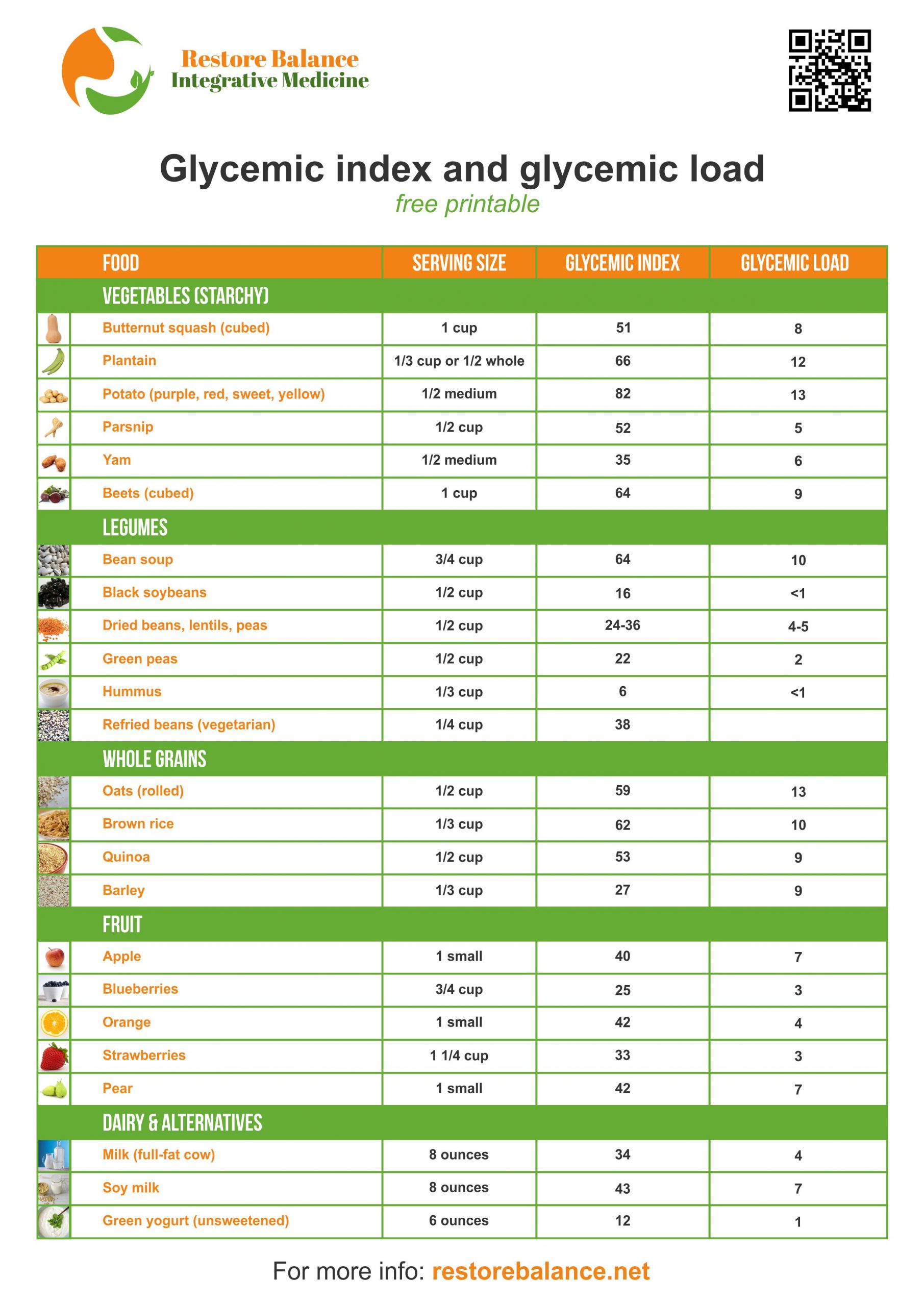
The green category are low glycemic load foods. Standard gl levels, per cassie. Web glycemic index (gi) is an objective way of measuring this effect. It is a sign of the quality of carbohydrates in the food. The glycemic load (gl) is a relatively new way to assess the impact of carbohydrate consumption on the rise of blood sugar in the body.
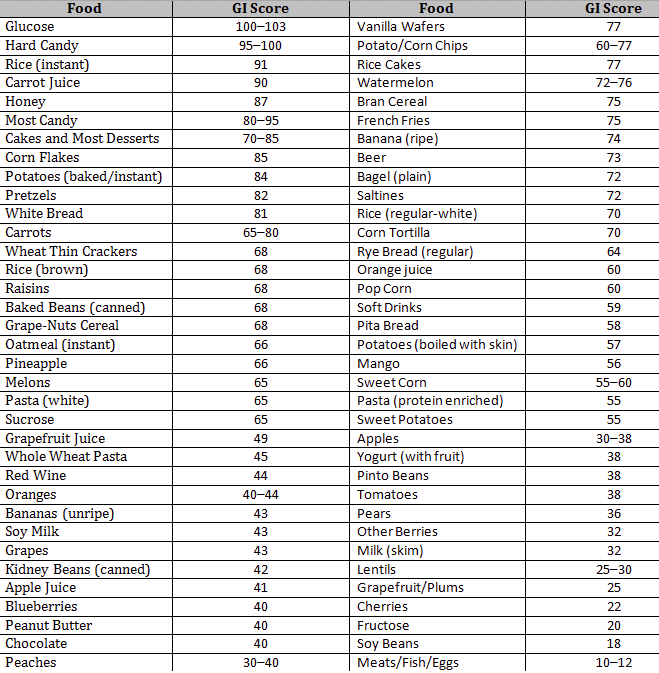
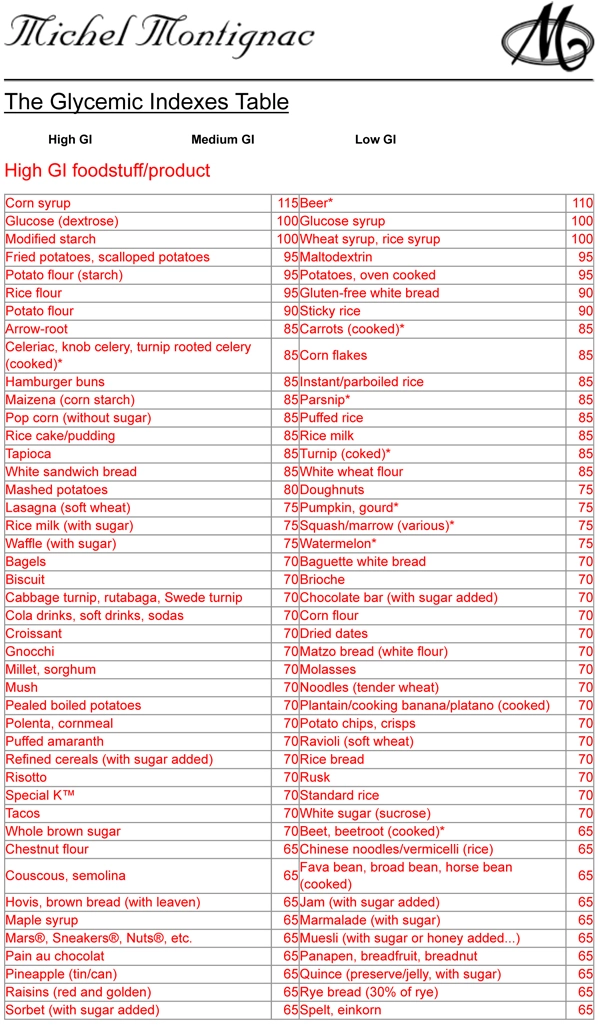
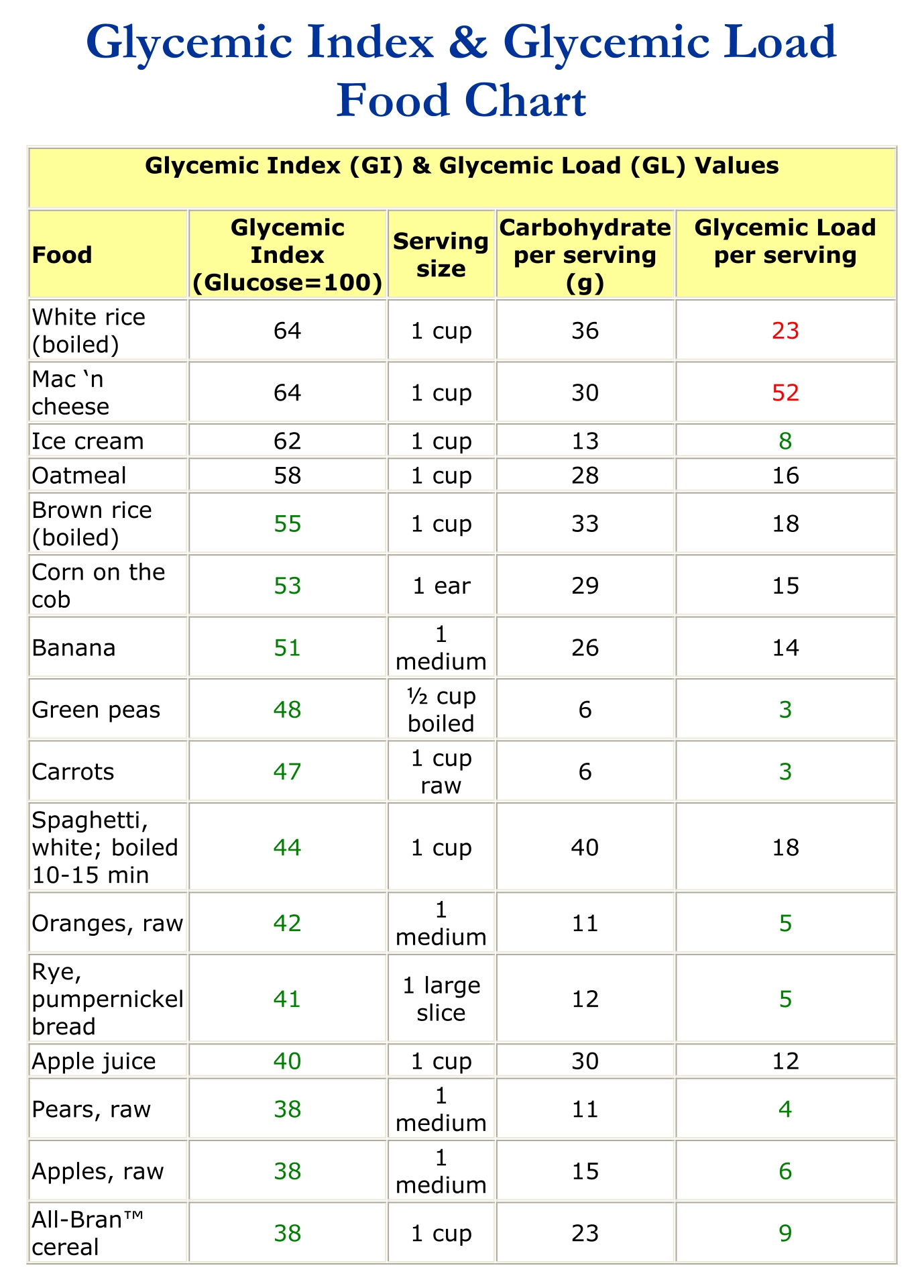
It is a sign of the quality of carbohydrates in the food. Eating foods with a lower gi may result in a more gradual rise in your blood sugar level. Food or drink by how muchit raises blood sugar levels a. Web the glycemic index (gi) is a measure of how fast a food raises the blood sugar level. Web the glycemic index chart below uses a scale of 1 to 100 for glycemic index and 1 to 50 for glycemic load values, glucose having the highest gi value of 100 and gl of 50. Red = stop and think. Gi chart for 600+ common foods that is updated constantly. Reliable tables of glycemic indexes (gis) and glycemic loads (gls) are critical to research examining the relationship between glycemic qualities of carbohydrate in foods, diets, and health. Low glycemic foods slow down sugar absorption, helping in maintaining stable glucose levels. For instance a food with a glycemic index of 30 doesn’t raise the blood glucose that much at all , but gi doesn’t consider how big the serving size is or how much you eat. The glycemic load (gl) is a relatively new way to assess the impact of carbohydrate consumption on the rise of blood sugar in the body. The green category are low glycemic load foods. Web below are downloadable glycemic load food lists. Web the glycemic index is a system of ranking foods on a scale of 0 to 100 according to how high blood glucose peaks within two hours of consuming the specific food. Web what are the glycemic index and glycemic load of your favorite foods?
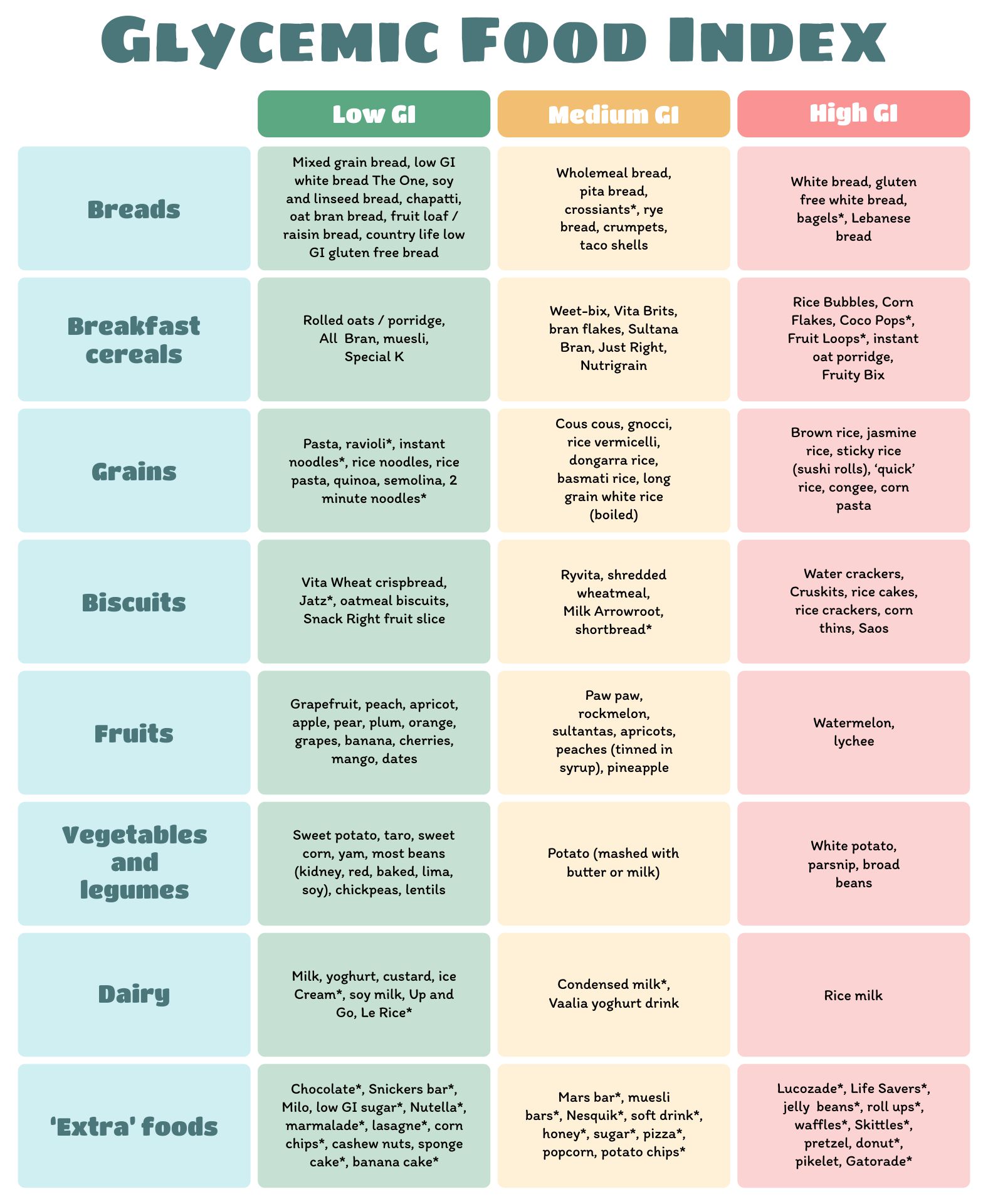
Foods Are Categorized As Low Gi (55 Or Less), Medium Gi (56 To 69) And High Gi (70 Or More).
Blood glucose is most stable when foods you eat have a glycemic index less than 50%. Web the glycemic index (gi) is a measure of how fast a food raises the blood sugar level. Eating foods with a lower gi may result in a more gradual rise in your blood sugar level. Red = stop and think.
Web Below Are Downloadable Glycemic Load Food Lists.
It is a sign of the quality of carbohydrates in the food. Foods with a higher gi value are more likely to spike your blood sugar than foods with a lower gi. It gives a fuller picture than gi alone. Web food vegetables (starchy) legumes whole grains fruit dairy & alternatives butternut squash (cubed) plantain potato (purple, red, sweet, yellow) parsnip
The Gi Of White Rice Was 75% Of The Glucose Gi.
Web complete up to date table of glycemic index values collected from all available studies. Keep this chart bookmarked in your browser for easy reference. The red are high glycemic load foods. Web the glycemic index chart below uses a scale of 1 to 100 for glycemic index and 1 to 50 for glycemic load values, glucose having the highest gi value of 100 and gl of 50.
The Yellow Are Medium Glycemic Load Foods.
Low glycemic foods slow down sugar absorption, helping in maintaining stable glucose levels. Reliable tables of glycemic indexes (gis) and glycemic loads (gls) are critical to research examining the relationship between glycemic qualities of carbohydrate in foods, diets, and health. Web glycemic index (gi) is an objective way of measuring this effect. There are three gi categories: