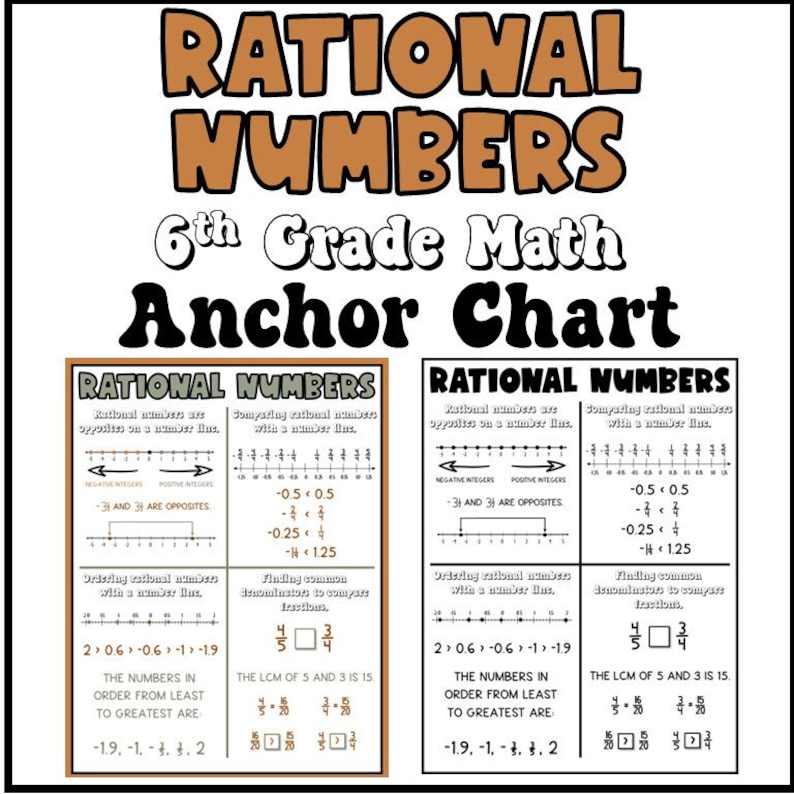
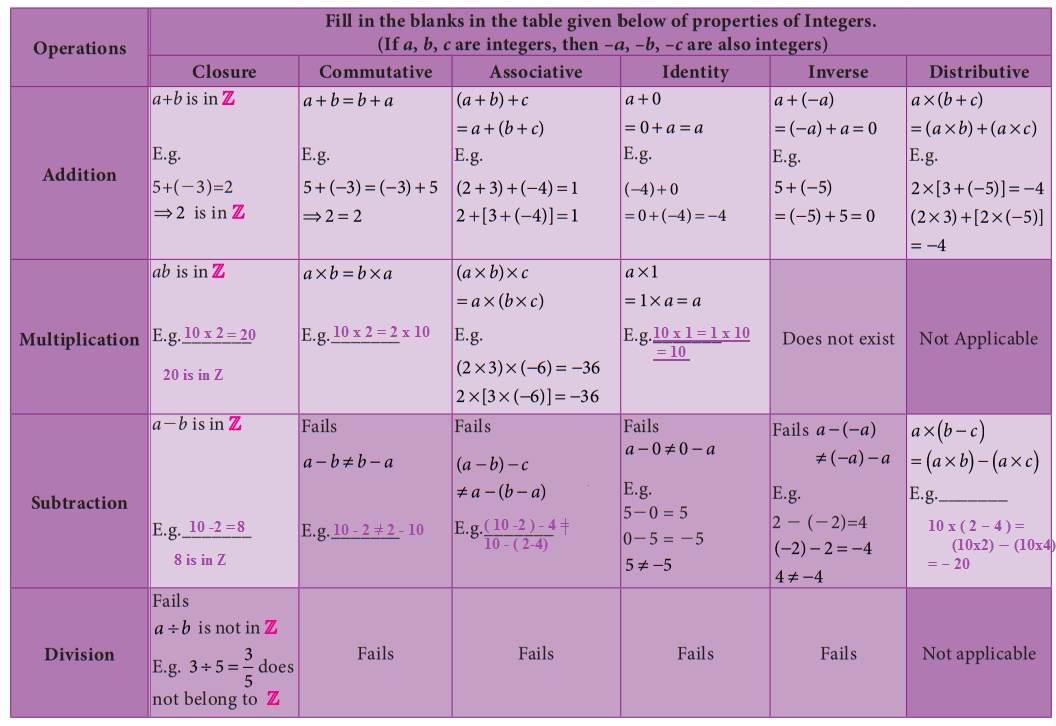
The np chart requires rational subgroups of consistent sample sizes. What is a rational number example? Rational numbers follow the rules of arithmetic and all rational numbers can be reduced to the form \(\frac{a}{b}\), where \(b\neq0\) and \(\gcd(a,b)=1\). Rational numbers on number line. This does not hold true for subtraction or division.
Let us learn more here with examples and the difference between them. Let us go through all the properties here. This does not hold true for subtraction or division. Web a rational number is a number. However, basic calculators can't give us answers in fractions.
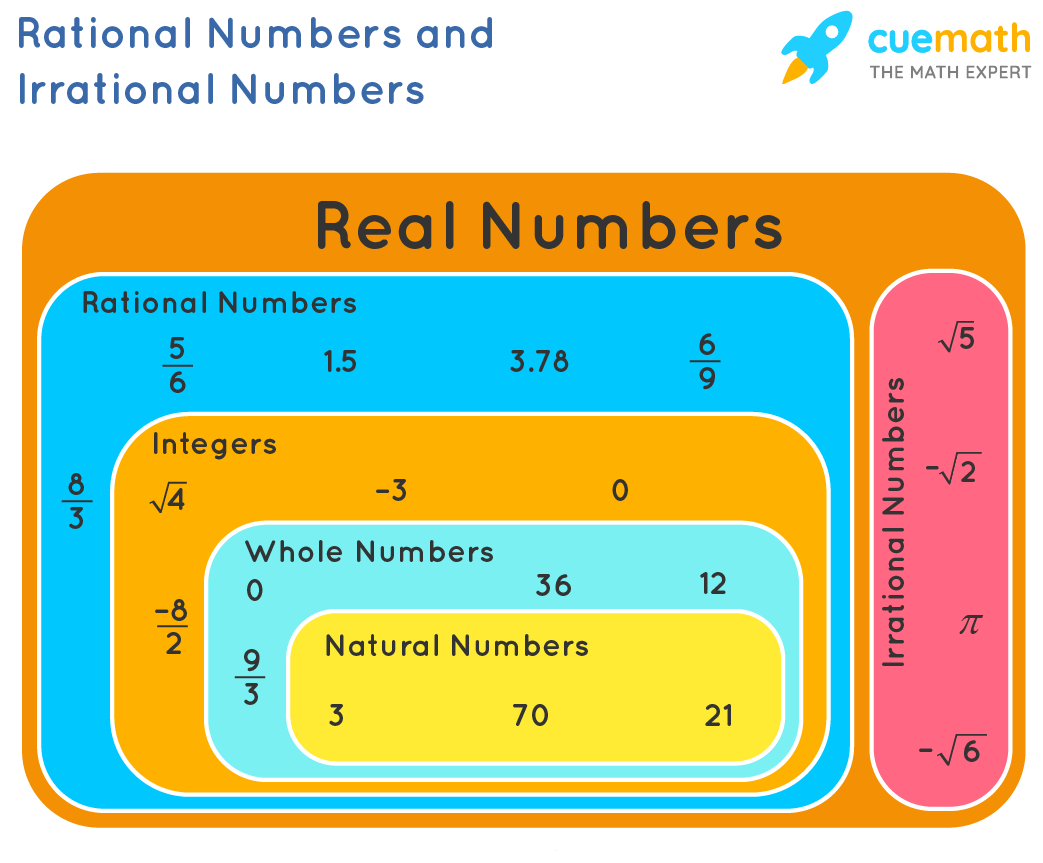
Web a rational number can be made by dividing two integers. The term rational in reference to the set refers to the fact that a rational number represents a ratio of two integers. For integers and decimals, we can rely on our calculators to add, subtract, multiply, and divide them. Convert rational numbers between decimal and fraction form. The number ½ is a rational number because it is read as integer 1 divided by integer 2.
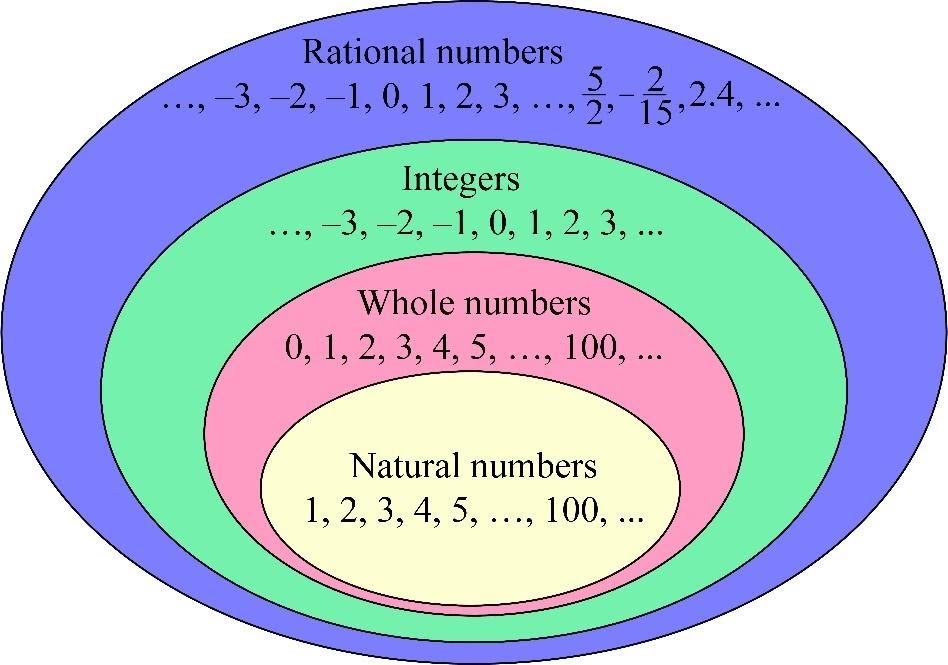
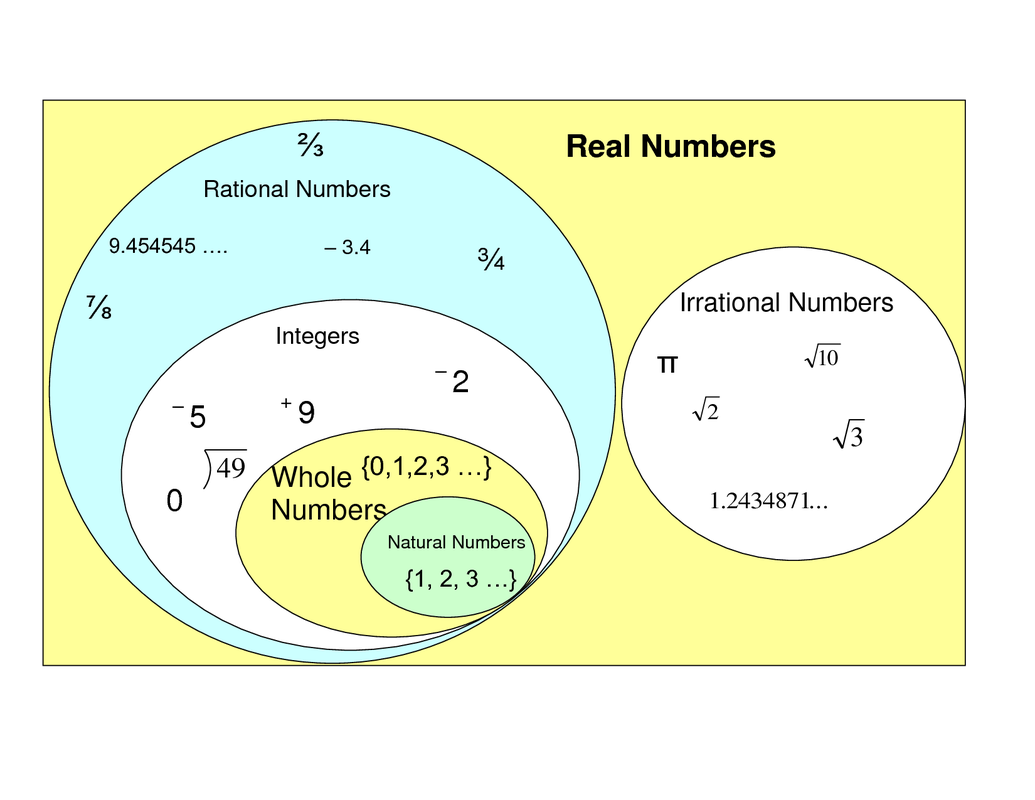
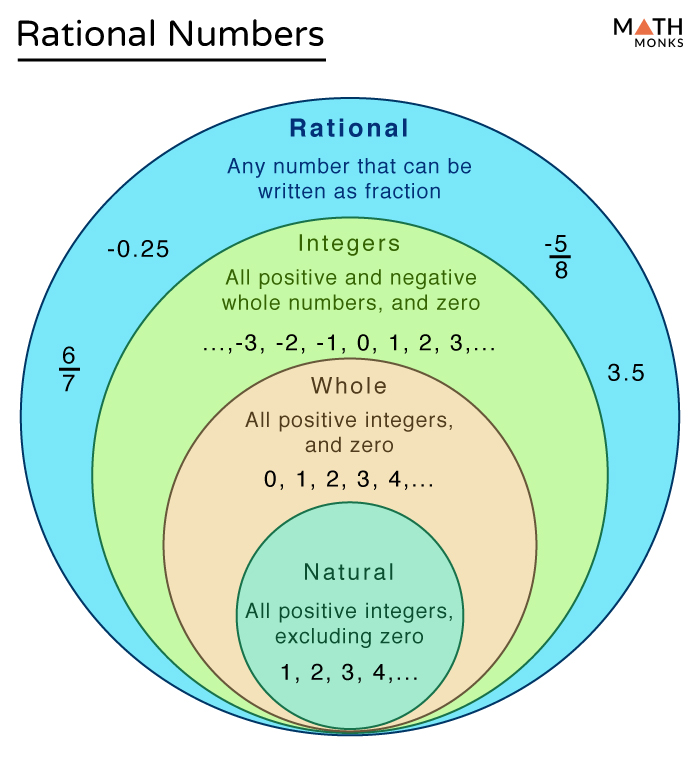
Sample size and subgroup size. But an irrational number cannot be written in the form of simple fractions. The adjective rational sometimes means that the coefficients are rational numbers. Some key fundamental concepts around np charts include: What is a rational number example? Rational numbers are numbers expressed in the form \frac {p} {q} where p and q are integers and p\neq q. Web what are rational numbers? Basically, the rational numbers are the fractions which can be represented in the number line. Web a rational number can be made by dividing two integers. Web rational numbers, irrational numbers, and roots: Rational numbers, irrational numbers, and roots: The venn diagram below shows examples of all the different types of rational, irrational numbers including integers, whole numbers, repeating decimals and more. All the numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Let us go through all the properties here. Numbers like 0, 1, 2, 3, 4,.
The Difference Between Rational Numbers And Fractions Lies In The Fact That Fractions Cannot Have Negative Numerator Or Denominator.
Rational numbers follow the rules of arithmetic and all rational numbers can be reduced to the form \(\frac{a}{b}\), where \(b\neq0\) and \(\gcd(a,b)=1\). A b, b ≠ 0 a b, b ≠ 0. Web a rational number is a number that can be represented as a fraction pq of two integers such that denominator q≠0. For integers and decimals, we can rely on our calculators to add, subtract, multiply, and divide them.
This Is The Basic Definition Of A Rational Number.
Web the np chart plots the number of defective units or nonconforming units in each sample or subgroup. Comparing irrational numbers with a calculator. Using negative numbers to make sense of contexts Web rational numbers are the numbers which can be represented in the form of p/q, where q is not equal to 0.
It Is A Rational Number Because It Can Be Written As:
Sample size and subgroup size. Where p and q are integers and q is not equal to zero. Where p and q are integers, and q ≠ 0. Let us learn more here with examples and the difference between them.
Rational Numbers Class 8 Notes.
The sample or subgroup size (n) should be constant across the chart. Web a rational number is the one which can be represented in the form of p/q where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0. Rational numbers are numbers expressed in the form \frac {p} {q} where p and q are integers and p\neq q. Some key fundamental concepts around np charts include: