Web bearing capacity factors are empirically derived factors used in a bearing capacity equation that usually correlates with the angle of internal friction of the soil. (1) strip foundation of width b (terzaghi, 1943) where: Ultimate bearing capacity for shallow foundations according to terzaghi. Web the bearing capacity of the soil is the maximum average contact pressure between the foundation and the soil which should not produce shear failure in the soil. Web the values provided in this table have been adjusted for overburden pressure, embedment depth, water table height, or settlement problems.
The bearing capacity of soil is the maximum average contact pressure between the foundation and the soil which should not produce shear failure in the soil. Ultimate bearing capacity is the theoretical maximum pressure that can be supported without failure. Web the formula for bearing capacity of soils gives engineers a way of accounting for the forces of the underlying soil when creating buildings. Web values of safe bearing capacity. For soils classified as ch or mh, without either torque probe values or blow count test results, selected anchors must be rated for a.
For preliminary design purposes, bs 8004 [1] gives typical values of allowable bearing capacity which should result in an adequate factor of safety against shaer failure without accounting for the setllemenet criteria [2]. Web the following steps outline how to calculate the soil bearing capacity. Web the footing ultimate bearing capacity was slightly increased as the embedment depth was increased. Web the ultimate bearing capacity depends on the size and shape of the loaded area, the depth of the loaded area below the ground surface, groundwater conditions, the type and strength of foundation materials, and the manner in which the load is applied. This is the ultimate bearing capacity of soil shown in table.
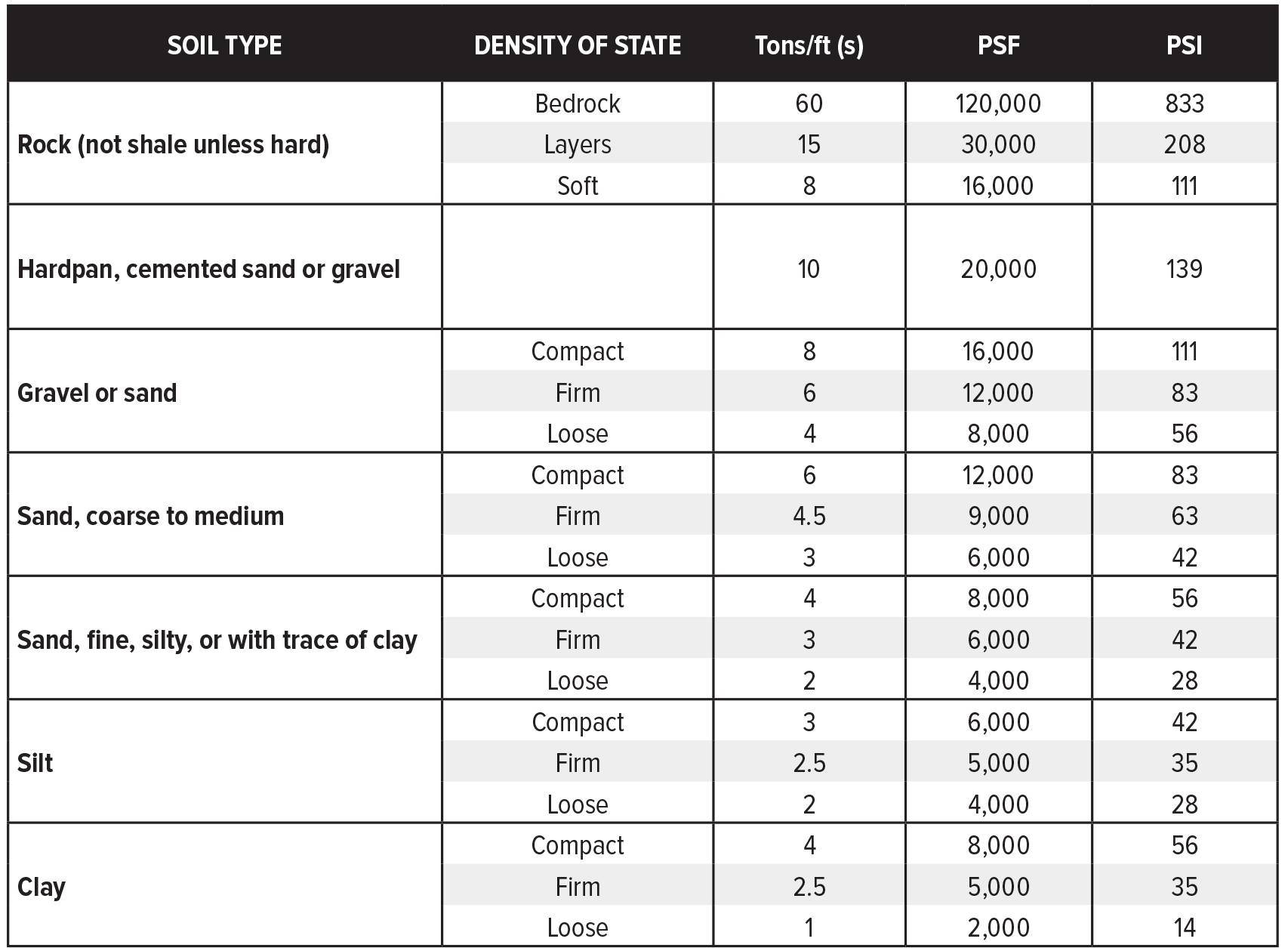
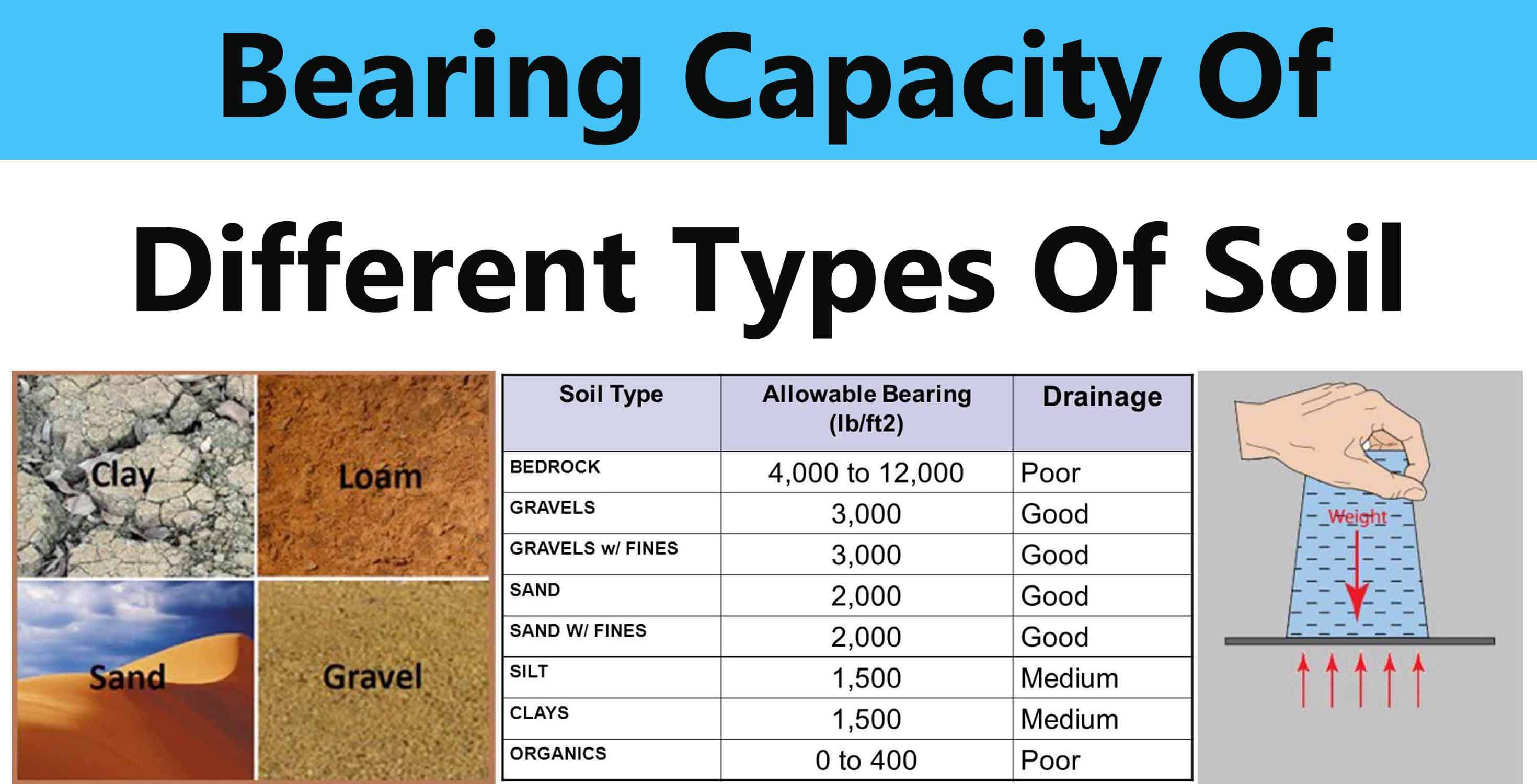
See a chart of soil bearing capacities for bedrock, sand, clay and more. For preliminary design purposes, bs 8004 [1] gives typical values of allowable bearing capacity which should result in an adequate factor of safety against shaer failure without accounting for the setllemenet criteria [2]. It determines the maximum allowable load that can be applied to the soil without causing significant settlements or foundation failure. Ultimate bearing capacity is the theoretical maximum pressure that can be supported without failure. The safe bearing capacity of soil should be determined on the basis of soil test data or by performing some field test such as standard penetration test or plate load test etc. Web the bearing capacity of soil is defined as the capacity of the soil to bear the loads coming from the foundation. Web the civilweb soil bearing capacity calculation excel suite comes complete with a 74 page ultimate design guide which includes a large variety of published typical soil bearing capacity values based on national standards, design guides and academic articles. This is the ultimate bearing capacity of soil shown in table. The soil bearing capacity chart can help. Web a soil bearing capacity chart is designed to provide engineers with a quick reference for the maximum load that various soil types can support. Web free online bearing capacity calculator. (1) strip foundation of width b (terzaghi, 1943) where: Web typical values of soil bearing capacity. Web the formula for bearing capacity of soils gives engineers a way of accounting for the forces of the underlying soil when creating buildings. Web for a strip foundation, the ultimate bearing capacity is given by the equation:
Web The Footing Ultimate Bearing Capacity Was Slightly Increased As The Embedment Depth Was Increased.
Web the bearing capacity of the soil is the maximum average contact pressure between the foundation and the soil which should not produce shear failure in the soil. Web the bearing capacity of soil is defined as the capacity of the soil to bear the loads coming from the foundation. Web in nontechnical engineering, bearing capacity is the capacity of soil to support the loads applied to the ground. This is the ultimate bearing capacity of soil shown in table.
Web Typical Values Of Soil Bearing Capacity.
Web the ultimate bearing capacity depends on the size and shape of the loaded area, the depth of the loaded area below the ground surface, groundwater conditions, the type and strength of foundation materials, and the manner in which the load is applied. The methods of determining bearing capacity of soils include theory and practical methods of measuring it. The soil bearing capacity chart can help. Dividing the ultimate soil bearing capacity by a safety factor we get the maximum safe bearing.
It Determines The Maximum Allowable Load That Can Be Applied To The Soil Without Causing Significant Settlements Or Foundation Failure.
See a chart of soil bearing capacities for bedrock, sand, clay and more. Next, determine the factor of safety. For preliminary design purposes, bs 8004 [1] gives typical values of allowable bearing capacity which should result in an adequate factor of safety against shaer failure without accounting for the setllemenet criteria [2]. These charts typically categorize soils into different types, such as clay, silt, sand,.
Web Values Of Safe Bearing Capacity.
Ultimate bearing capacity for shallow foundations according to terzaghi. Web the strength and compactness of soil is important when pouring concrete footings. The increase in the length of the reinforcement and friction angle of the backfill soil has given some improvement in the ultimate bearing capacity, while an increase in the width of the footing decreased the bearing capacity. Web the capacity of the soil to allow the loads coming from the foundation is called bearing capacity of the soil.