Web learn the definition and diagram of marginal cost, the cost of producing an extra unit. When 1 pie i s produced, the marginal cost is $1. Web the chart shows the marginal cost and marginal revenue of producing apple pies. For this company, the $15. We find the point where marginal revenue equals marginal cost, which is 9,000 gallons.
It costs cool clothes company $15 to produce one pair of jeans, but they needed to discontinue production of shirts to focus on jeans. Web learn the definition and diagram of marginal cost, the cost of producing an extra unit. See how marginal cost changes with the law of diminishing marginal returns. Web the graph shows the marginal cost of producing soccer cleats for sabrina's soccer. The cost of producing additional quantity.
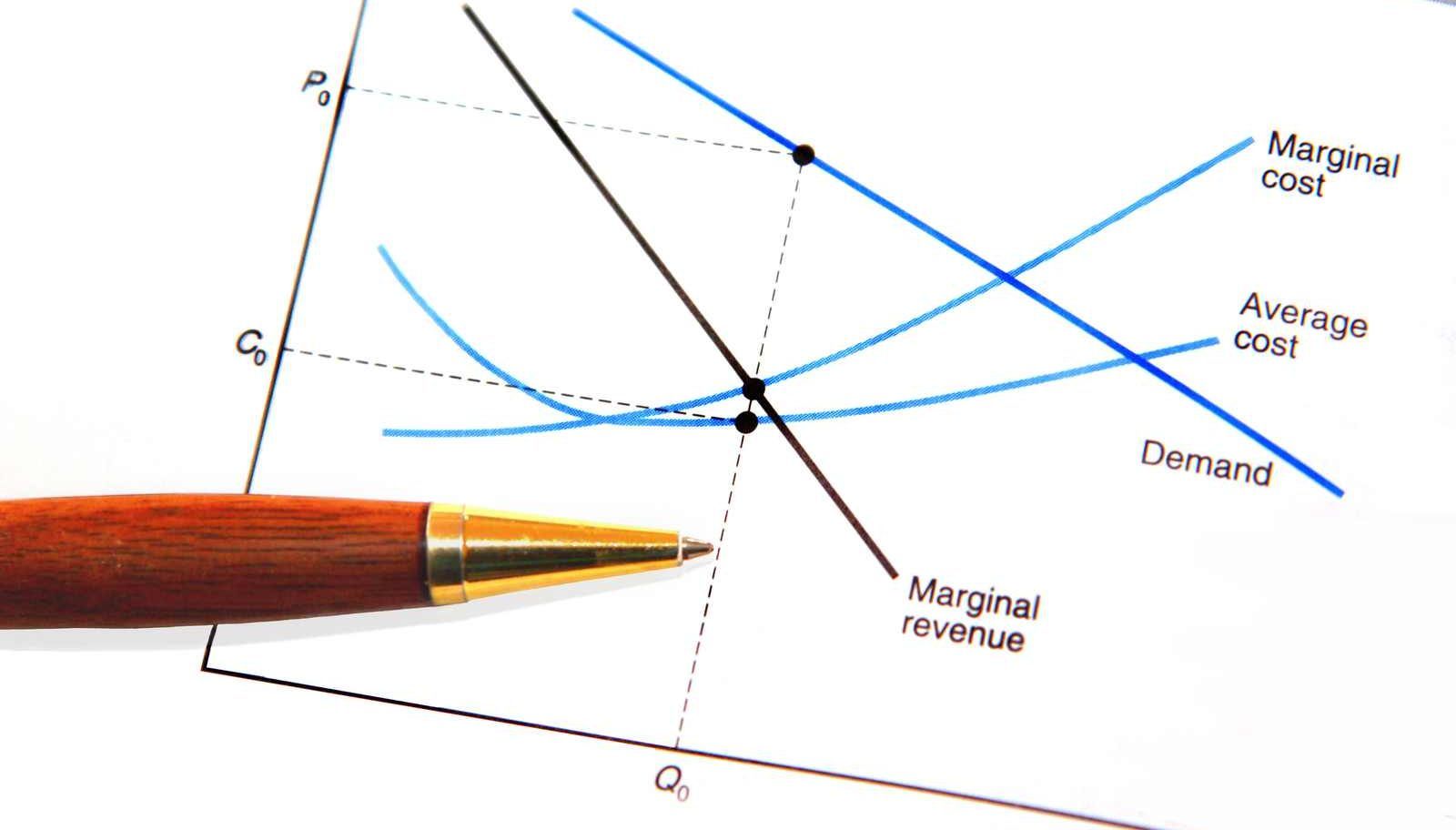
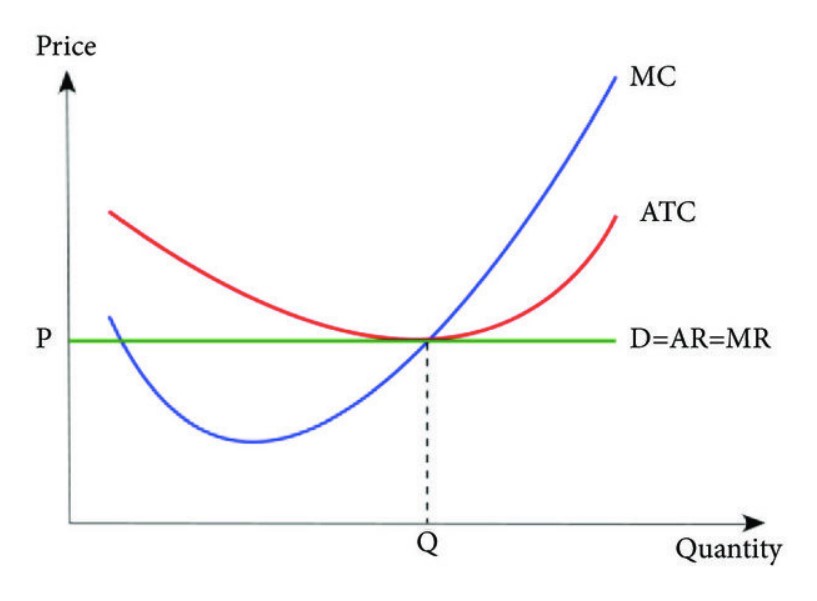
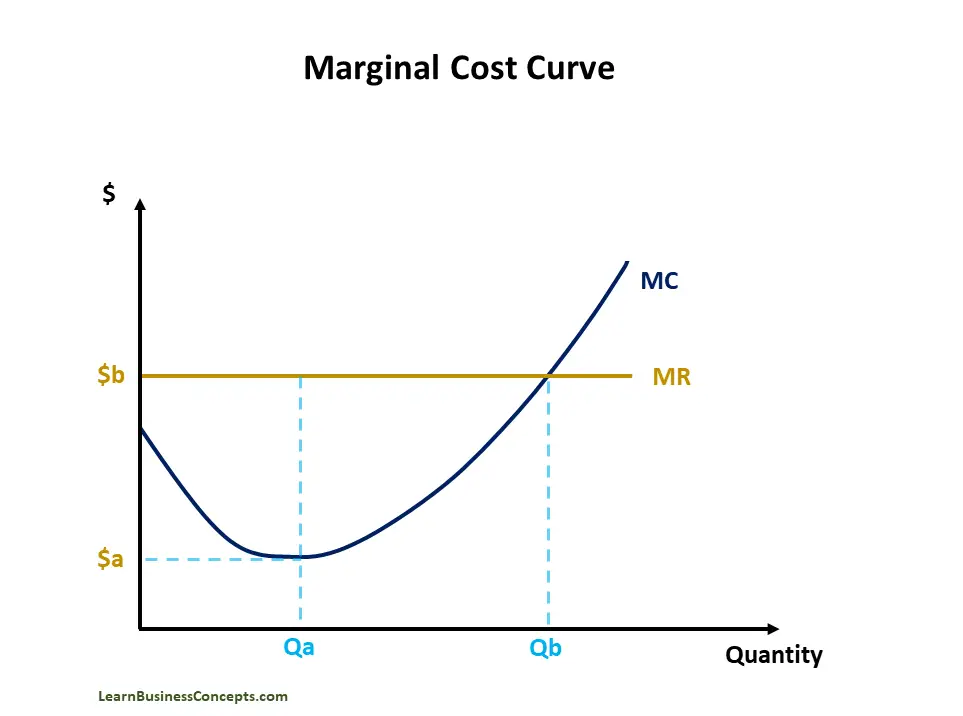
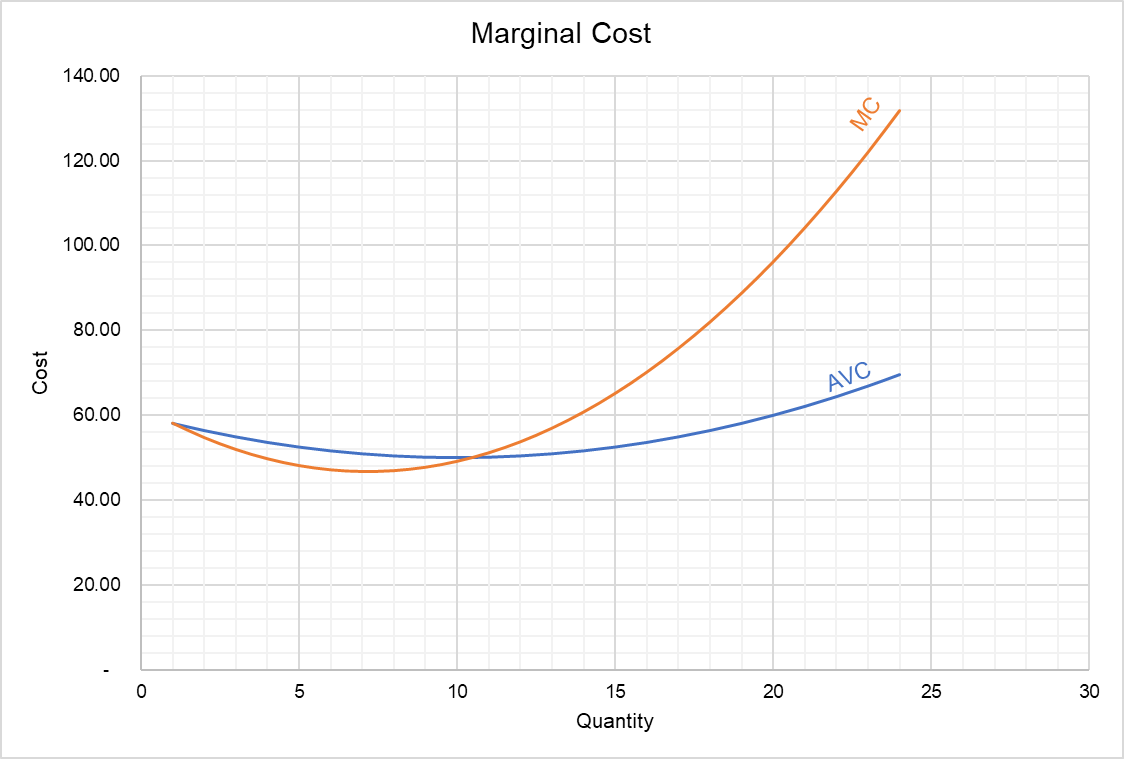
See how marginal cost changes with the law of diminishing marginal returns. At which level of production does the company make the most profit? This chart demonstrates that the marginal cost initially decreases as production increases. See how marginal cost, average cost, fixed cost, variable cost and total cost are related. Web the market price is 50 cents per gallon, and we want to maximize profit.
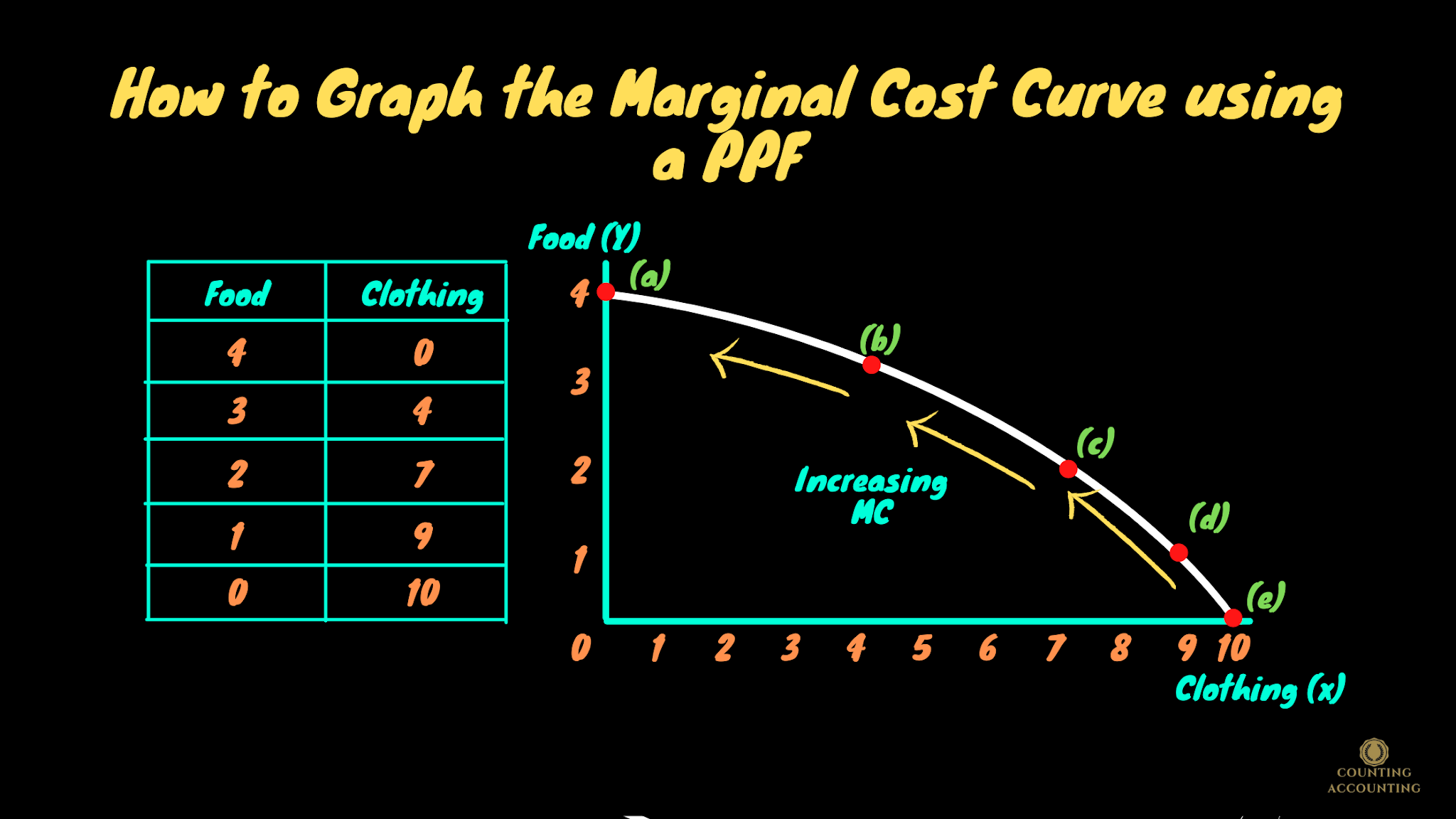
For this company, the $15. See how to graph these curves and highlights their intersections, which represent minimum points for average. This chart demonstrates that the marginal cost initially decreases as production increases. Web the graph shows the marginal cost of producing soccer cleats for sabrina's soccer. Web learn the definition and diagram of marginal cost, the cost of producing an extra unit. Web from the chart, the marginal cost of producing each number of pie is shown. Create columns for units produced, fixed cost, variable cost, and total. See the marginal cost curve and its shape, and compare it with marginal benefit. When two pies were made,. Web to find marginal cost, first make a chart that shows your production costs and quantities. Opportunity cost is the amount of money that. We find the point where marginal revenue equals marginal cost, which is 9,000 gallons. Web in this video we calculate the costs of producing a good, including fixed costs, variable costs, marginal cost, average variable cost, average fixed cost, and average total cost. The marginal cost starts to gradually rise starting with the fourth pie. Web the chart shows the marginal cost and marginal revenue of producing apple pies.
See How Cost Curves Help Firms Maximize Profits And Policy Makers Make.
When two pies were made,. Opportunity cost is the amount of money that. Web from the chart, the marginal cost of producing each number of pie is shown. The cost of producing additional quantity.
Create Columns For Units Produced, Fixed Cost, Variable Cost, And Total.
Web to find marginal cost, first make a chart that shows your production costs and quantities. At which level of production does the company make the most profit? Web the marginal cost initially declines up to the third pie, in the pie production graph. For this company, the $15.
Web Marginal Cost Is The Additional Cost Of Producing One More Unit Of A Good Or Service.
Web from the given chart, you can observe that the marginal cost initially decreases as production increases, which means that producing the second and third. Marginal cost refers to the cost of producing an. This chart demonstrates that the marginal cost initially decreases as production increases. We find the point where marginal revenue equals marginal cost, which is 9,000 gallons.
Web Learn How Changes In Fixed And Variable Costs Affect Marginal Cost, Average Variable Cost, Average Fixed Cost, And Average Total Cost With Graphs And Examples.
Web learn how to draw and interpret cost curves for short run and long run. Web learn how to derive and interpret cost curves, including marginal cost, in the short run and long run. See the marginal cost curve and its shape, and compare it with marginal benefit. Web the market price is 50 cents per gallon, and we want to maximize profit.